Title:HEAT LOSS AND COOLING CORRECTIONS AND SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF BAD CONDUCTOR
APPARATUS: Calorimeter with outer racket for lagging stirrer, thermometer 0-100c,beaker,rubber bung,stop watch thread, chemical balance and weight.
Aim:To determine the cooling corrections and specific heat capacity of a bad conductor
Diagram
Theory:heat loss is the loss of heat to the environment in heat experiment involving calorimeter,heat loses always occour.
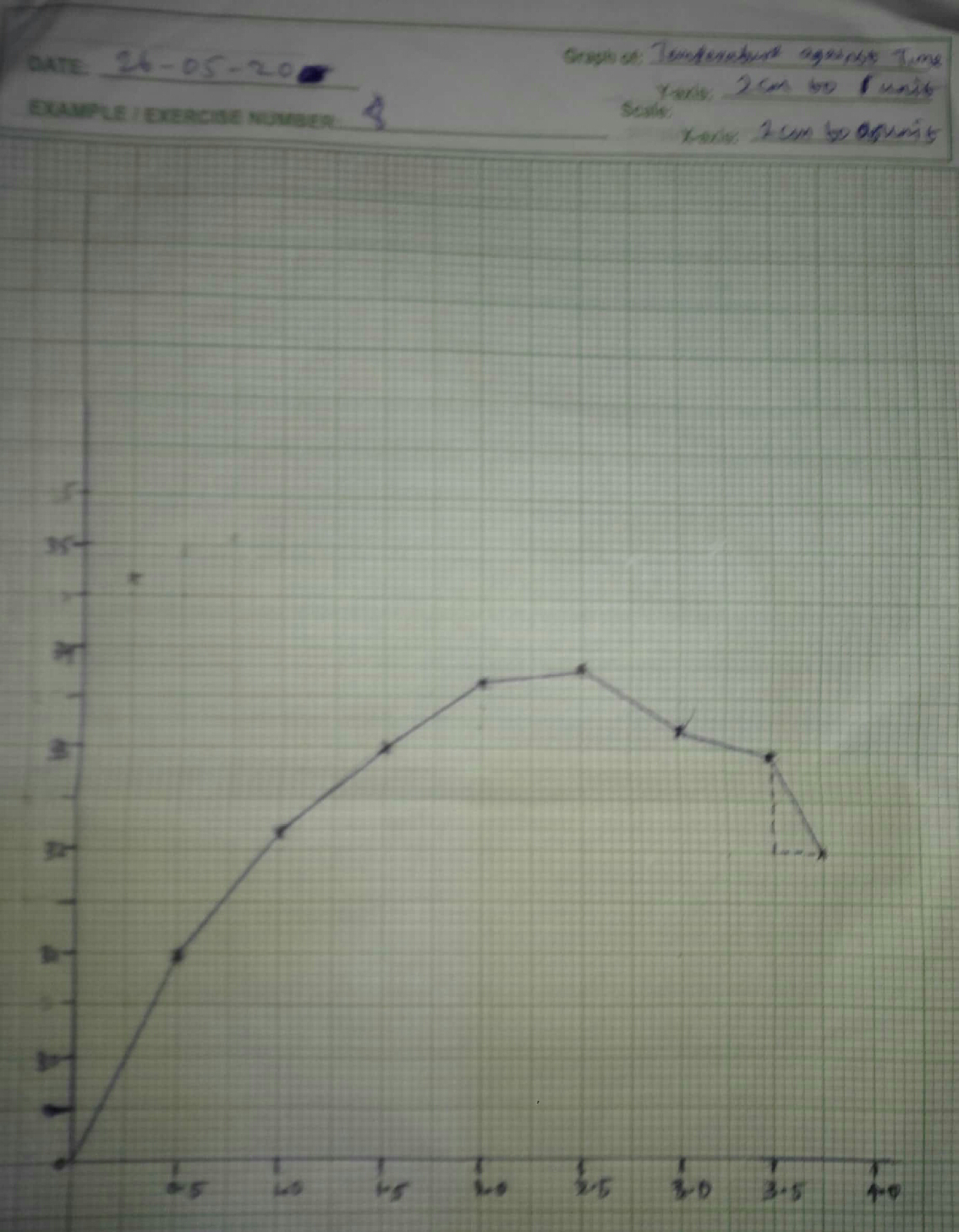
The minimum and maximum temperature recorded would be at variance with the corresponding values,if heat loss does not occur,this is the cooling correction to me made.
Specific heat capacity of a conductor is the temperature needed to raise 1k
It is given as
MCtitan equal to H
Where m=mass,c=specific heat capacity, titan,=change in the temperature, H=amount of heat.
PROCEDURE OF SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF BAD CONDUCTOR
The rubber bung was weighed and was suspended in a boiling water,then the calorimeter and the stirrer was weighed and also re -weighed when it was half filled with water ,the temperature of the calorimeter and it's content was then recorded and the rubber bung had been in the boiling water for at least half an hour.
The timer was started immediately, while it was stirred continuously,the temperature was recorded at half minutes intervals until the temperature had reached it maximum and had fallen again by 2 to 3°c.
PRECAUTIONS OF HEAT LOSS AND COOLING CORRECTIONS AND SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF BAD CONDUCTOR
(1)The calorimeter was lagged and polished to prevent heat loss to the environment
(2)The calorimeter was always stirred continuously to allow for even spread of temperature.
(3)The thermometer used was in the right range of calibration to prevent wrong reading temperature.
Room temperature= 26.5
Mass of Calorimeter and Stier = 90g = 0.09kg
Mass of rubber bung = 27g = 0.027kg
Mass of calorimeter + stirrer + water = 178 = 0.178kg
Statement of results
From the experiment concluded, it was brought to our notice that the higher the S.H of an object, the higher the thermal energy needed to be transferred to the object to raise the temperature.
DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
on conducting the experiment, it was noticed that there was a gradual increase in temperature after constant storing of the calorimeter at a particular intak.
It was discovered that there was a steady temperature range and thereafter the temperature decreased gradually .




Comments
Post a Comment